Health November 3, 2025
Timing Medication Doses: How Administration Time Affects Side Effects
Medication Timing Calculator
Medication Timing Assessment
Enter medication name and your scheduled time to see if your dose timing is optimal.
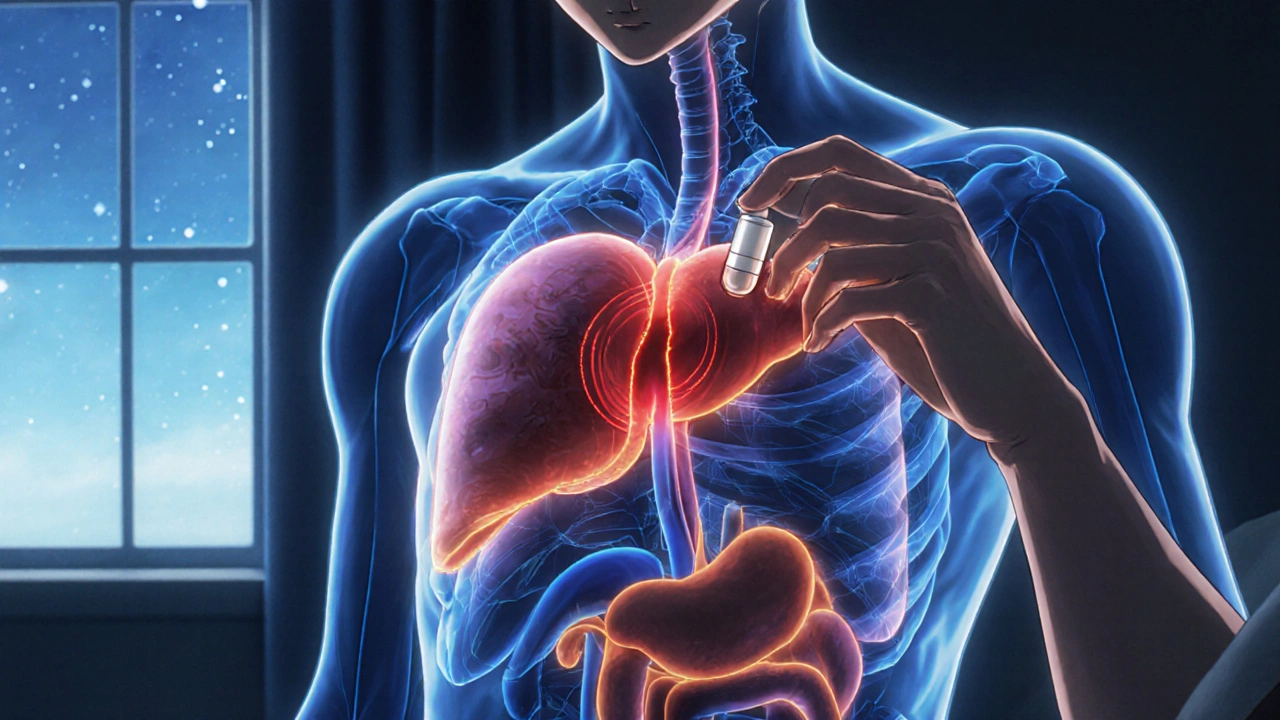
What if taking your pill five minutes earlier or later could mean the difference between feeling fine and ending up in the hospital? It’s not a hypothetical. For many medications, timing isn’t just a suggestion-it’s a safety rule.
Why Timing Matters More Than You Think
Your body runs on a 24-hour clock. Every hour, your liver processes drugs differently. Your kidneys filter them faster or slower. Hormones rise and fall. Blood pressure dips at night. Cholesterol production peaks in the early morning. These rhythms aren’t background noise-they directly affect how your body handles medication. Take statins, for example. If you take them at night, you reduce LDL cholesterol 15-20% more than if you take them in the morning. Why? Because your liver makes most of its cholesterol while you sleep. Taking the drug when production is highest means it blocks more of it. That’s not magic-it’s biology. Same with blood pressure meds. People who take ACE inhibitors or ARBs at bedtime cut their risk of heart attack or stroke by nearly 30% compared to those who take them in the morning. The MAPEC study tracked over 2,000 patients for six years. The bedtime group had fewer cardiovascular events, even though both groups took the same dose. The only difference? When they took it.When Timing Goes Wrong: The Real Cost of Mistakes
Timing errors don’t always cause immediate disasters. But they add up. Studies show that 43% of medication orders have some kind of timing discrepancy. That’s nearly half of all prescriptions. For some drugs, being 30 minutes late is no big deal. Hydrochlorothiazide, a common diuretic, can be given up to 12 hours off schedule with little impact. But for others? A 10-minute delay can mean trouble. Insulin is one. If you take rapid-acting insulin too early before eating, your blood sugar can crash. Too late, and it spikes. One study found that 22% of insulin timing errors led to hypoglycemia-enough to send someone to the ER. Anticoagulants like warfarin are another. Being off by even an hour can raise bleeding risk by up to 37%. That’s not theoretical. Real patients, real bleeds, real hospital stays. And then there’s chemotherapy. Deviations of more than 30 minutes reduce drug effectiveness by 15-20%. That’s not just discomfort-it’s survival. In cancer care, timing isn’t about convenience. It’s about whether the treatment works at all.High-Risk Medications That Demand Precision
Not all meds need perfect timing. But some absolutely do. Here’s the short list of drugs where minutes matter:- Insulin - Mistimed = hypoglycemia risk up to 22%
- Warfarin and other anticoagulants - Timing errors increase bleeding risk by up to 37%
- Chemotherapy agents - 30+ minute delays cut efficacy by 15-20%
- Morphine for cancer pain - Must be given within 10-15 minutes of scheduled time to avoid breakthrough pain and withdrawal symptoms
- Beta-blockers - Evening dosing reduces post-surgery atrial fibrillation by nearly 40%

Why Hospitals Struggle to Get It Right
You’d think hospitals would nail this. After all, they’re staffed with nurses, pharmacists, and tech systems designed to prevent errors. But the reality is messier. A study found that with just five interruptions during a medication pass, error rates jumped from 39% to 61%. Five. That’s it. A phone call. A family member asking a question. A code blue down the hall. Each one breaks focus. And timing slips. IV medications are especially vulnerable. Up to 53% of IV errors involve timing. Oral meds? Around 8-25%. That’s because IVs are often given in rapid succession, under pressure, with little room for error. Even worse? Many electronic health record systems treat all meds the same. They don’t distinguish between “flexible” and “critical” timing. A nurse gets a reminder to give metformin at 8 a.m. and warfarin at 5 p.m. But the system doesn’t say: “Warfarin must be given within 15 minutes. Metformin? You’ve got two hours.”What Works: Real Solutions That Reduce Errors
The good news? Solutions exist-and they’re working. Barcode medication administration (BCMA) systems cut timing errors by 28%. When a nurse scans a patient’s wristband and the drug’s barcode, the system checks if it’s the right time, the right dose, the right patient. If not, it stops the process. New tools like Epic’s ChronoCare module (launched in 2023) flag high-risk meds and warn staff if a dose is outside its safe window. For example, if someone tries to give insulin at 2 a.m. instead of 7 p.m., the system pops up: “This dose is outside the recommended window. Confirm override?” Hospitals that trained staff on chronotherapy saw error rates drop from 35% to 12% in under two months. It’s not about hiring more nurses. It’s about changing how you think about time.
What You Can Do at Home
You’re not in a hospital. But you still need to get timing right. Start by asking your pharmacist or doctor: “Does the time I take this medicine matter?” If they say no, ask why. If they say yes, ask: “What’s the window? Can I take it an hour early? What if I’m late?” Use alarms. Not just your phone. A pillbox with built-in lights or a smart dispenser that beeps when it’s time. One study found that patients using timed reminders were 68% more likely to take their meds correctly. Don’t assume your schedule fits the drug. If you work nights, taking a morning-only pill at 8 a.m. might not work. Talk to your doctor about switching to evening dosing if possible. And if you’re caring for someone else? Write it down. Put it on the fridge. Set a shared calendar. Timing errors happen most often when caregivers are tired, stressed, or juggling multiple responsibilities.The Future Is Personalized Timing
This isn’t just about clocks. It’s about your genes. The ChronoGene study, wrapping up in late 2024, is testing whether variations in your circadian clock genes affect when your body responds best to drugs. One person might metabolize beta-blockers fastest at 6 a.m. Another at 10 p.m. That’s not guesswork-it’s precision medicine. The FDA is pushing for this. In 2022, they reviewed chronopharmacology data in 17 new drug applications. In 2018? Just three. That’s a 500% increase in two years. By 2027, 65% of high-risk medications will have standardized timing protocols. That means your prescription might come with a note: “Take at 9 p.m. - this timing reduces side effects by 30%.”Bottom Line: Time Is a Dose
You wouldn’t skip a pill. You wouldn’t double up. So why treat timing like an afterthought? The science is clear: when you take your medicine matters as much as how much you take. For some drugs, it’s the difference between control and crisis. For others, it’s the difference between feeling okay and feeling great. Start asking questions. Start tracking times. Start treating timing like part of the prescription-not a footnote.Does the time I take my medication really affect side effects?
Yes, for many medications. Your body’s internal clock affects how drugs are absorbed, processed, and eliminated. Taking a statin at night, for example, can reduce cholesterol 15-20% more than taking it in the morning. For insulin, warfarin, or chemotherapy, timing errors can lead to serious side effects like low blood sugar, bleeding, or reduced treatment effectiveness.
Which medications are most sensitive to timing?
High-risk medications include insulin (mistimed doses cause hypoglycemia), anticoagulants like warfarin (timing errors raise bleeding risk by up to 37%), chemotherapy drugs (30+ minute delays reduce effectiveness by 15-20%), morphine for cancer pain (must be given within 10-15 minutes), and beta-blockers (evening dosing reduces post-surgery heart rhythm problems). Statins also benefit from nighttime dosing.
Can I take my pill an hour early or late?
It depends on the drug. For most routine meds like metformin or blood pressure pills, being an hour off is usually fine. But for insulin, anticoagulants, or chemo, even 15-30 minutes can matter. Always ask your pharmacist or doctor: “What’s the safe window for this medication?” Don’t assume it’s flexible.
Why do hospitals struggle with medication timing?
Nurses face constant interruptions-phone calls, family questions, emergencies-that break focus during med passes. Studies show just five interruptions can increase timing errors from 39% to 61%. Many electronic systems don’t distinguish between flexible and critical meds, treating all doses the same. IV meds are especially prone to timing errors, with up to 53% of mistakes involving timing.
How can I improve timing adherence at home?
Use alarms, smart pill dispensers, or a shared calendar. Ask your pharmacist if your meds have a flexible window. If you work nights or have an irregular schedule, talk to your doctor about adjusting the timing. Patients using reminders are 68% more likely to take meds correctly. Don’t rely on memory-write it down or set a digital alert.
Is chronotherapy just for hospitals?
No. Chronotherapy is for anyone taking medication regularly. While it’s more structured in hospitals, the same principles apply at home. Evening statins, nighttime blood pressure meds, and timed insulin are all forms of chronotherapy. The goal is simple: match drug action to your body’s natural rhythms to reduce side effects and boost effectiveness.
Write a comment
Items marked with * are required.






8 Comments
Clyde Verdin Jr November 5, 2025 AT 14:51
THIS IS WHY AMERICA IS FALLING APART. 🤡 People are taking insulin at 3 AM because their phone alarm went off and they were half-asleep. Hospitals don't even track this shit properly. I saw a nurse give warfarin at 8 AM instead of 8 PM... and the patient bled out. No one got fired. Just another Tuesday in the land of the free. 💀
Key Davis November 5, 2025 AT 18:03
I appreciate the thoroughness of this analysis. The scientific underpinnings of chronopharmacology are both elegant and profoundly consequential. It is imperative that healthcare providers, patients, and policymakers recognize that temporal precision is not ancillary-it is foundational to therapeutic efficacy and patient safety. A standardized protocol for high-risk medications should be universally adopted, with education integrated into medical curricula and public health campaigns.
Cris Ceceris November 6, 2025 AT 14:19
I’ve been thinking about this a lot lately. Like… why do we treat time like it’s just a number on a clock? Your body isn’t a vending machine-you don’t just drop in a pill and get the same result every time. It’s like your organs have their own schedule, and if you ignore it, they start giving you the silent treatment. I used to take my blood pressure med whenever I remembered… then I started taking it at bedtime like they said. My nights got quieter. My mornings felt less like a fight. I didn’t even realize how much I was struggling until I stopped.
Brad Seymour November 6, 2025 AT 17:46
Honestly, this is such a cool topic. I never realized how much biology and timing overlap like this. I work in pharmacy and we’ve started using ChronoCare at my hospital-it’s wild how many errors get caught before they happen. That said, I think we’re still underestimating how much this affects people at home. Maybe we need a ‘medication rhythm’ app? Like a Fitbit for your pills? 😄
Malia Blom November 7, 2025 AT 21:48
Ok but let’s be real-this whole ‘timing matters’ thing is just Big Pharma’s way of making you feel guilty for forgetting your meds. 😏 I mean, if your body can’t handle a 2-hour window, maybe the drug’s just poorly designed? Also, why are we still using warfarin when there’s NO MONITORING? Like, why not just switch to something that doesn’t require you to become a human lab technician? #PharmaScam
Erika Puhan November 7, 2025 AT 23:16
The systemic negligence in chronotherapeutic compliance is a glaring indictment of the neoliberal healthcare paradigm. The epistemic hegemony of institutional protocols, devoid of circadian epigenetic calibration, perpetuates iatrogenic morbidity. The absence of pharmacogenomic integration into EHRs represents a catastrophic failure of translational medicine. Furthermore, the reliance on consumer-grade alarm systems as clinical interventions is ontologically indefensible. This is not biohacking-it’s bio-negligence.
Edward Weaver November 9, 2025 AT 11:30
This is why America needs to stop letting foreigners run our hospitals. In my uncle’s village in Texas, they just give the meds when they remember-no fancy scanners, no ‘ChronoCare’ nonsense. We don’t need all this tech. You take your pills when you’re awake. If you die? Then you weren’t meant to live. This over-engineering is just making people paranoid. We used to be tougher. Now we’re all walking around with pillboxes like we’re in a sci-fi movie. 🇺🇸
Lexi Brinkley November 9, 2025 AT 21:10
I just started using a smart pillbox and it’s LIFE CHANGING. 🤯 I used to forget my insulin like 3x a week. Now it lights up, beeps, and even texts my mom if I don’t take it. I’ve had ZERO lows since. Also, I got my whole family on the same app so we can all see each other’s meds. 💪❤️ #MedicationWin